Optical Properties of Gallium Indium Antimonide (GaInSb)

Optical properties
Infrared refractive index (300 K)n=4.0-0.2x
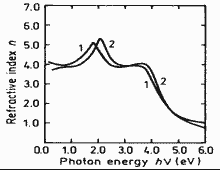 |
Refractive index n versus photon energy. 300 K 1. x=0 (InSb), 2. x=1 (GaSb) (Adachi (1989)). |
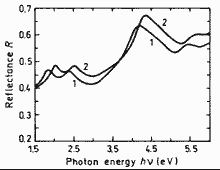 |
Normal incidence reflectivity versus photon energy. 300 K. 1. x=0 (InSb), 2. x=1 (GaSb) (Aspnes and Studna (1983)). |
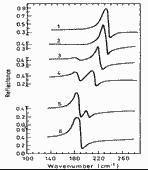 |
Wavenumber dependence of the reflectance for different alloy compositions. 300 K. 1. x=1, 2. x=0.84, 3. x=0.6 4. x=0.3, 5. x=0.05, 6. x=0 (Brodsky et al. (1970)). |
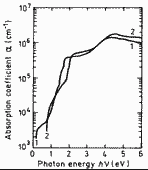 |
The absorption coefficient versus photon energy. 300 K. 1. x=0 (InSb), 2. x=1 (GaSb) (Aspnes and Studna (1983)). |
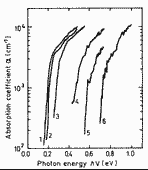 |
Intrinsic absorption edge for different alloy compositions of n-type (curves 1,2) and p-type (curves 3-6). 300 K. 1. x=0, 2. x=0.07, 3. x=0.36 4. x=0.7, 5. x=0.78, 6. x=0.97 For n-type samples electron concentration no~2·1017÷1018 cm-3. For p-type samples hole concentration po~1018÷6·1019 cm-3. (Rousina et al. (1990)). |
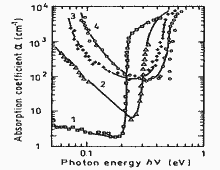 |
Absorption coefficient versus photon energy for different doping levels. x=0. (n-InSb). 130 K. no (cm-3): 1. 6.6·1013, 2. 7.5·1017, 3. 2.6·1018, 4. 6·1018. (Ukhanov (1977)). |
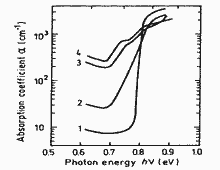 |
Absorption coefficient versus photon energy for different doping levels. x=1. (p-GaSb). 77 K. Na (cm-3): 1. 2.9·1017, 2. 5·1018, 3. 1.8·1019, 4. 3·1019. (Iluridze et al. (1987)). |