Mobility and Hall Effect of Gallium Indium Arsenide Phosphide (GaInAsP)
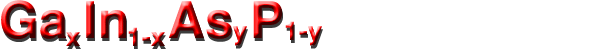
Electrical properties
Basic ParametersMobility and Hall Effect
Transport Properties in High Electric Fields
Impact Ionization
Recombination Parameters
Mobility and Hall Effect
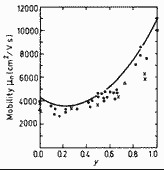 |
Electron mobility versus alloy composition parameter y for GaxIn1-xAsyP1-y lattice-matched to InP. T=300 K. The experimental points correspond to samples with electron concentration no=(1÷5)·1016 cm-3. Full curve shows calculations for no=1015 cm-3. ((Pearsall (1982)). |
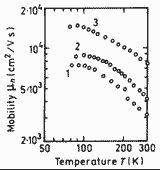 |
Electron mobility versus temperature for GaxIn1-xAsyP1-y alloys lattice-matched to InP. Electron concentration no=(1÷5)·1016 cm-3. 1. - y=0.31 2. - y=0.50 3. - y=0.91 (Pearsall (1982)). |
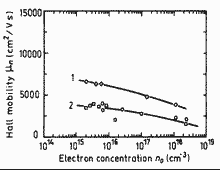 |
Electron Hall mobility versus electron concentration for three GaxIn1-xAsyP1-y alloy compositions lattice-matched to InP. T=300 K 1. - y=0.9 (λ=1.55µm) 2. - y=0.6 (λ=1.3µm, circles) and y=0.3 (λ=1.1µ, squares). (Tappura (1993)). |
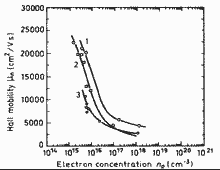 |
Electron Hall mobility versus electron concentration for three GaxIn1-xAsyP1-y alloy compositions lattice-matched to InP. T=77 K 1. - y=0.9 (λ=1.55µm) 2. - y=0.3 (λ=1.3 µm) 3. - y=0.6 (λ=1.3 µm) (Tappura (1993)). |
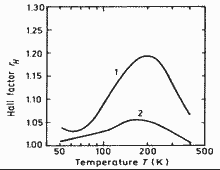 |
Hall factor for n-type Ga0.47In0.53As (y=1) versus temperature. 1. - no=1015 cm-3; 2. - no=1017 cm-3. (Pearsall (1982)). |
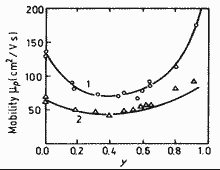 |
Hole mobility versus alloy composition parameter y for GaxIn1-xAsyP1-y lattice-matched to InP. T=300 K. 1. - po=4·1016 cm-3; 2. - po=2·1018 cm-3. (Pearsall (1982)). |
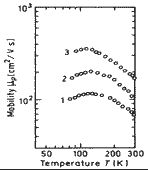 |
Hole mobility versus temperature for GaxIn1-xAsyP1-y lattice-matched to InP. 1. - y=0.64 2. - y=0.8 3. - y=0.91 (Hayes et al. (1982)). |